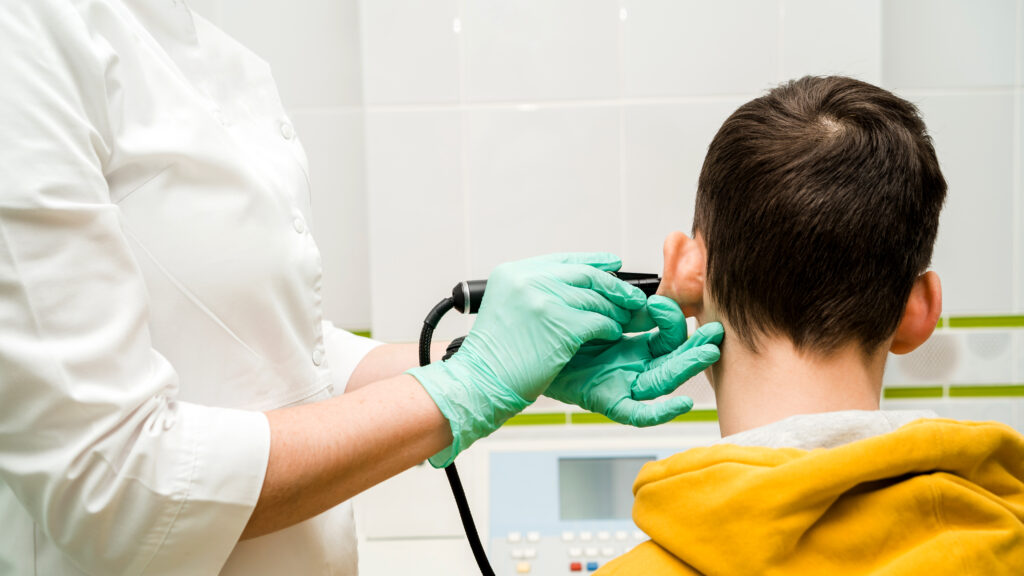
On a cold October night a decade in the past, doctor Michael Cohen arrived at Boston’s Logan Worldwide Airport lugging a hefty contraption, constructed like a tiny tank, that instantly drew the eye of airport safety officers. It was a tool to detect ear issues, and he and a colleague have been hauling it across the globe — first on a redeye to Frankfurt, adopted by Khartoum, after which on to Addis Ababa.
The system — known as a tympanometer — was too dear for a lot of well being care suppliers worldwide to afford on their very own, so Cohen, an otolaryngologist at Massachusetts Eye and Ear, was shuttling it to colleagues in Ethiopia.
Now, a gaggle of engineers and listening to specialists are working to sort out that hole head-on. They’re designing tympanometers which can be low cost sufficient and sufficiently small to seek out their manner into the palms of practically any supplier who wants one. In a preliminary new examine, printed final month in Communications Medication, the researchers report that their smartphone-based system carried out practically in addition to commercially out there tympanometers that may price 1000’s of {dollars}.
commercial
“That is the form of product that’s preferrred for a resource-constrained setting the place this data would simply in any other case be unavailable,” mentioned Cohen.
The tympanometer is likely one of the many units within the armamentarium of ear, nostril, and throat medical doctors and audiologists, who give attention to listening to and collaborate intently with otolaryngologists. A tympanometer vibrates the eardrum after which measures the sound it displays, testing how effectively the ear strikes. That detected sound reveals physicians whether or not the eardrum is functioning appropriately. Fluid within the ear, a punctured eardrum, and irregular bone development all present up on the graphs generated by tympanometers.
commercial
The primary particularly, which is usually an indication of an infection, is a giant drawback that may trigger listening to loss and diminished listening to. Center ear infections are among the many most typical causes {that a} household will go to a major care supplier and it’s estimated that over half of all toddlers will develop such an an infection yearly. Particularly in childhood, any kind of listening to loss is a good larger drawback, as toddlers depend on their sense of sound to know language and proceed regular improvement.
“Tympanometry is one thing that’s used on a regular basis in otolaryngology and audiology visits. It’s a part of routine care,” mentioned Randall Bly, an otolaryngologist at Seattle Kids’s Hospital and the College of Washington and a senior writer on the brand new examine. “And it’s prohibitively costly in lots of cases.”
Tympanometers are costly, usually working between $2,000 to $5,000. There are already moveable tympanometers in the marketplace which can be smaller than the normal mannequin Cohen was utilizing, however they, too, can price 1000’s of {dollars}. In designing the brand new mannequin, the researchers particularly needed to dramatically lower down the prices of utilizing the know-how in routine care whereas retaining accuracy. In a examine with 50 kids, the smartphone-based software gave outcomes much like these delivered by industrial units in 86% of instances.
And importantly, the researchers printed the code on-line and purposefully didn’t patent the know-how, which permits others to construct on and use the work freely.
“This exploits the economies of scale that smartphones have (which comes with processors, shows and all types of {hardware} sensors) that doesn’t exist with these diagnostic medical units,” mentioned Shyam Gollakata, a professor on the College of Washington and senior writer of the paper, in an e mail. “I feel this is a crucial course we have to probe for a number of medical situations in order to democratize medical units and make them accessible to all components of the world.”
The brand new system makes use of an affordable speaker, microphone, motor, and strain sensor to duplicate the mechanism of current tympanometers, which insert a Q-tip-like probe into the ear, play a sound, and report the sound reflecting from the eardrum. (This additionally entails measurements at completely different pressures within the ear canal, made attainable by a syringe and the strain sensor.) General, the design is compact. By comparability, the tympanometer that Cohen took to Ethiopia weighed the equal of 6 gallons of water.
To construct it, the researchers scoured patents and took aside tympanometers they purchased on eBay. Probably the most difficult step was creating an hermetic seal, mentioned the examine authors, which concerned testing many alternative supplies and adhesives to get it proper. “I believed it was fairly cool as a result of they’ve to have the ability to change air strain within the ear,” mentioned Beth Prieve, an audiologist and professor at Syracuse College who research the center ear and was not concerned within the examine.
The pandemic disrupted the timeline of the examine, because it quickly paused affected person recruitment. It additionally narrowed the pool of potential contributors, as a result of fewer youngsters have been coming in to have their ear infections handled.
Past portability, one of many major strengths of the brand new system is its worth — a mere $28 on prime of the smartphone. Excessive price of different tympanometers is a priority shared by different physicians. Brian Westerberg, who travels to Uganda practically yearly for medical work, in contrast the worth for tympanometers to the excessive price of sure listening to aids. “The anecdotal phrase on the road is that every one the {hardware} in that, you possibly can purchase for a number of hundred {dollars}. And it’s all analysis and improvement, and the title, and the software program actually that you’re paying for,” mentioned Westerberg, a neurotologist at Windfall Well being Care in Canada. With tympanometers, he mentioned, “I’m undecided analysis and improvement prices you’ll be able to put in there as a result of all of that know-how has been round for many years.”
“There has not been a lot current innovation in tympanometer units within the final decade or so,” Gollakata mentioned. “The medical system business has had no competitors.”
The units are largely ill-suited to the mud and grime outdoors of in-hospital clinics. “They are usually delicate, getting knocked round, and so they should be calibrated too frequently,” mentioned Westerberg. Bigger units are additionally onerous to convey to colleges or transport in a cellular clinic. That’s the reason Westerberg sees the open supply insights from the brand new analysis as so worthwhile. “It appears very altruistic,” mentioned Westerberg. “They simply appear to be in it to enhance entry to care, which is a refreshing, refreshing perspective.”
The researchers hope that their system can be used and improved upon in lower-resource areas. It’s an interesting prospect for physicians who apply in these areas.
“The outcomes that they’ve and the accessibility they’d give to very low useful resource nations, it might actually assist to keep away from all the issues of not having a analysis of listening to loss or issues that give listening to loss,” mentioned Amarilis Meléndez, head of the Division of Otorhinolaryngology at Hospital Santo Tomás in Panama.
It may be helpful in different areas the place well being care is troublesome to entry. “Whether or not you’re in the US or Canada, there are nonetheless pockets of people that do not need good entry to care,” mentioned Westerberg. “And this know-how, this cellular know-how, actually is permitting individuals to take it nearer to house.”
Westerberg has personally skilled this. “I simply obtained an e mail the opposite day from a household doc who’s up in Haida Gwaii,” an archipelago off of Canada’s west coast “manner out by the Alaska border,” he mentioned. By analyzing footage the native physician despatched, he was in a position to save the affected person a “three-hour flight down and all the prices to the well being care system related to that.” That’s not all the time attainable, nevertheless, as a result of even for consultants, visible examination will not be fool-proof. “I take a look at ears all day lengthy and there’s some areas that I simply battle to inform: Is there fluid there or not?” mentioned Westerberg. He wants a tympanometer in these cases to determine between completely different however important remedy choices.
However extra work lies forward, together with to make the units helpful for infants, who’ve softer ear canals. The traditional frequency that works for older kids and adults doesn’t work for them. A better frequency, which was not examined within the examine, would carry out higher as a substitute. “I want to see [this] completed in one other examine,” mentioned Meaghan Reed, Director of Scientific Audiology at Massachusetts Eye and Ear.
Physicians and the examine authors alike additionally level out the necessity for extra analysis, together with experiments involving care suppliers who will not be specifically educated and apply in numerous components of the world. “I’d be very keen to check this product,” mentioned Titus Ibekwe, head of the Division of Otorhinolaryngology on the College of Abuja in Nigeria. He mentioned the primary examine is “sufficient to attract an anecdotal conclusion, however not a conclusive one.” Gollakata mentioned there are additionally plans to check the system in Kenya.
Specialists mentioned that for the know-how for use extra broadly, there may be additionally a necessity to make sure that there are suppliers educated to make use of it and the specialists to deal with the issues that get identified. “In some locations, you don’t have sufficient assets of ENTs to see the sufferers,” mentioned Meléndez, utilizing an acronym that refers to otolaryngologists. A 2019 examine that she co-authored discovered a big disparity within the variety of otolaryngologists inside Latin America, with as few as 50 of those specialists in Guatemala, a rustic with 17.7 million individuals. The low variety of otolaryngologists is an issue in her house nation of Panama too, Meléndez mentioned.
Specialists added that use of the brand new, smartphone-based tympanometers isn’t sufficient to shut gaps in entry. Gadgets reminiscent of audiometers and electroencephalograms are needed for pinpointing different hearing-related issues and conducting common listening to screenings for newborns, which the World Well being Group recommends. “However the tools will not be there, in order that turns into the limitation,” mentioned Ibekwe. Audiometers, that are used for listening to checks, are much more costly, costing as a lot as $12,000, Westerberg mentioned. “That’s only a nonstarter for someplace like Uganda,” he mentioned.
The researchers already see their work making an impression, although. “Beforehand should you needed to do that, it’d be a variety of pink tape and forms to attempt to purchase a tympanometer and order a tympanometer,” mentioned Justin Chan, a Ph.D. scholar on the College of Washington and first writer of the examine. “However now we’ve got one thing that any person can simply obtain off the web and doubtlessly construct and assemble. And that’s a functionality that has not been completed earlier than.”