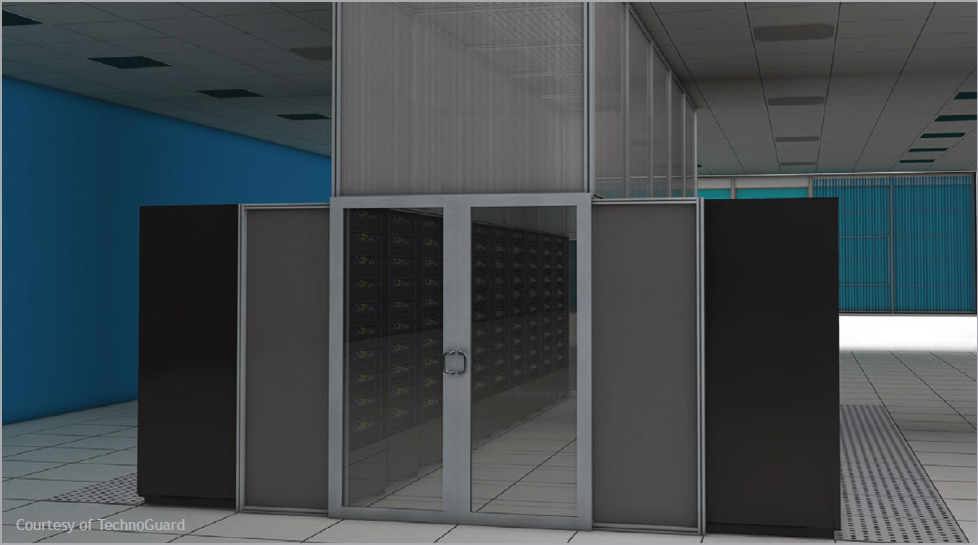
Irrespective of how nicely a containment system is
constructed and put in, its advantages will be decreased or negated if good “rack hygiene” practices usually are not adopted. (Supply: TechnoGuard)
As energy densities in every information middle cupboard grows, so have the challenges of protecting IT gear cool. Whereas liquid cooling is commonly talked about as the one answer for the longer term, others are engaged on pushing the capabilities of air cooling. This launches our article collection on excessive density IT cooling.

Get the total report.
Information facilities have seen an ongoing enhance in common energy density, particularly over the previous decade. Furthermore, the ability density per IT cupboard has seen a good larger enhance as IT Tools (ITE) energy density continues to rise to ranges that appeared excessive just a few years in the past, however are actually the brand new regular. Now we have main ITE producers which supply normal “commodity” 1U servers with 800 to 1,800 watt redundant energy provides which might require greater than 1000 watts of cooling.
That is being pushed by processor and IT gear producers which in flip are being held again as a result of most mainstream information facilities are onerous pressed or unable to help greater than 10-15 kW per rack. Processor energy ranges are escalating from 100 to 250 watts and chip producers have product roadmaps for CPUs and GPUs which might be anticipated to exceed 500 watts per processor within the subsequent few years.
This development has left many questioning if air-cooled ITE has reached its energy limits and if liquid cooling is admittedly the one long run answer. At the moment, some HPC IT gear is out there as liquid or air cooled variations, nevertheless the majority of ordinary off-the-shelf ITE continues to be air cooled. And the vast majority of new mainstream information facilities proceed to be designed for air cooled ITE.
In actuality, there are a number of points that affect how excessive the ability density in air-cooled IT gear in normal cupboards will be pushed. This has led to renewed efforts by ITE producers and information middle operators to push the boundaries of air cooling.
There are a number of points that affect how excessive the ability density in air-cooled IT gear in normal cupboards will be pushed. This has led to renewed efforts by ITE producers and information middle operators to push the boundaries of air cooling.
The fundamental rules of knowledge middle cooling are well-known; take away the warmth load generated by IT gear and switch it through a number of bodily mediums (air, liquids, or solids) and one in all extra types of thermo-mechanical techniques to reject it out of the ability. Nevertheless, as energy densities of IT processors and different computing associated elements elevated, this course of has turn into harder to perform successfully and effectively. For functions of this report, we’ll talk about air and liquid cooling, with a main deal with air-cooled IT gear.
Energy Density – Watts per What?
One of many extra frequent points that get mentioned is what’s the energy density restrict for air cooled ITE. Information middle energy density is usually expressed as common watt per SF. That is calculated primarily based on the important energy out there to the IT Load (watts or kilowatts), divided by the cooled space occupied by the ITE (whitespace). Nevertheless, this doesn’t actually mirror the situations of the cooled area occupied by the air-cooled IT gear.
Within the instance under, we’ll study a hypothetical 10,000 sq. foot whitespace space of a fringe cooled raised ground information middle. The important load ranking is 1,000 kW and 200 IT Cupboards at 5, 7.5 and kW common energy.
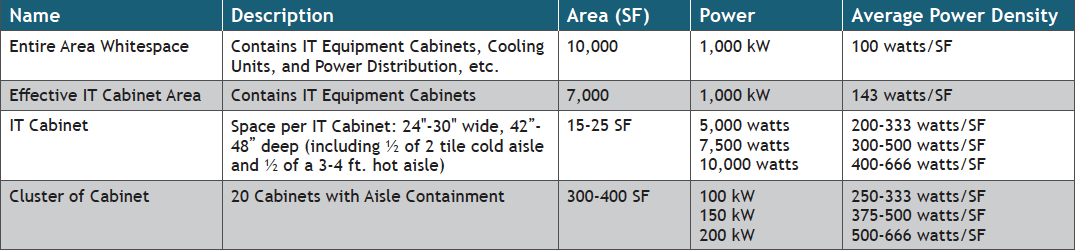
Desk 1 – Common energy density by space
Air vs Liquid Cooling
The 2 best sources of warmth in IT gear are the processors (CPU, GPU, TPU, and so on.) and reminiscence. As talked about, processor energy ranges are escalating from 100 to 250 watts and chip producers have product roadmaps for CPUs and GPUs which might be anticipated to exceed 500 watts per processor within the subsequent few years (see AHSRAE Processor roadmap) and symbolize 50% or extra of the ITE warmth load. Whereas the ability degree of working reminiscence chips (DIMM, and so on.) are comparatively low compared, the full quantity of reminiscence has elevated considerably and continues to rise, and may symbolize 20% or extra of the warmth load.
As talked about, liquid cooling is being primarily used to deal with the upper energy processors. Whereas there are a lot of variations of liquid cooling applied sciences and methodologies, they often fall into three classes:
- Liquid Cooling for Air-Cooled ITE
- Liquid Cooled ITE
- Immersion Liquid Cooling
Liquid Cooling for Air-Cooled ITE
The ITE is normal unmodified gear. The method begins on the processor chip and the warmth is usually transferred to an hooked up air-cooled warmth sink. All the warmth is transferred to room primarily based cooling models, or to shut coupled cooling: Inrow cooling, Rear Door Warmth Exchanger (RDHX) or different varieties similar to overhead aisle primarily based cooling models.
Liquid Cooled ITE
The method begins with inner elements; the processor chip and reminiscence the warmth is usually transferred to an hooked up liquid cooled warmth sink (chilly plate), additionally typically known as direct liquid cooling. Usually, a portion (50-75%) of the warmth is transferred to a liquid loop, the rest of the warmth goes to room primarily based cooling models, or to shut coupled cooling: Inrow, RDHX, or different related techniques.
Immersion Liquid Cooling
All the ITE is submerged in a dielectric fluid, which engulfs the chassis and all of the elements. Just about all the warmth is successfully transferred to the fluid. These are generalized summaries of three classes. Every have benefits, limitations and trade-offs, nevertheless the extra granular facets of Liquid Cooled ITE and Immersion cooling raises the complexity, (as a result of varies methodologies, fluid varieties and working temperatures), which makes additional dialogue of those elements past the scope of this text collection.
Crossing Thermal Boundaries – Chip to Environment
With a purpose to higher perceive the problems, you will need to study the trail, thermal boundaries and comply with how the warmth is transferred from the chip to the exterior warmth rejection techniques. Beginning on the processor chip, there may be usually about 1 to 1.5 sq. inches on the prime of the case that should switch 100-150-200 watts of warmth to an hooked up warmth sink (built-in warmth spreader) through conduction (successfully 7,000 to 14,000 watts/SF). From there, a number of followers draw consumption air from the entrance of the IT gear case, directing it to the fins of the warmth sink although the gear chassis, and likewise cooling the opposite IT elements after which exhausted out of the rear of the ITE case. For a typical fashionable 1U server with multi-processors, drawing 500 watts it might require 80-100 CFM to chill it.
When the case solely has a really restricted space (2-4 sq. inches) for the air to enter and exit the openings, the result’s comparatively excessive airflow velocities and pressures within the IT cupboard.
Nevertheless, the case solely has a really restricted space (2-4 sq. inches) for the air to enter and exit the openings. This ends in comparatively excessive airflow velocities and pressures within the IT cupboard. When (40) 1U servers are stacked in a typical 42U cupboard, this creates one other set of challenges (see extra about this within the Rack Hygiene part within the remaining installment of our particular report article collection).
Obtain all the paper, “Excessive Density IT Cooling – Breaking the Thermal Boundaries“ courtesy of TechnoGuard, to study extra. In our subsequent article, we’ll take a deeper have a look at the physics of airflow.