Story
June 23, 2022

Navy funding – not just for conventional long-life missions but additionally for nontraditional shorter life, lower-cost small satellite tv for pc purposes – continues to develop. Radiation-hardened element designers are working to fulfill the diminished dimension, weight, energy, and value (SWaP-C) calls for of those new missions whereas sustaining radiation tolerance and coping with the supply-chain complications that proceed to plague the electronics business.
Sturdy progress within the radiation-hardened (rad-hard) element enviornment is due partially to the rising adversarial menace in house from nations like China, which motivates extra funding from the U.S. Division of Protection (DoD). Mounting demand may also be ascribed to the success of lower-cost New Area purposes like small satellites (small sats) and Low Earth Orbit (LEO) megaconstellations or satellite tv for pc swarms.
Proof of that motivation is seen the Air Drive Fiscal Yr 2023 DoD funds request, which gives elevated funding for the Area Drive. Examples of that funding, in line with the Air Drive, are the funding request for $987 million for house expertise improvement and prototyping missile warning/monitoring in addition to the $1 billion requested for floor and house segments of the Subsequent-Era Overhead Persistent Infrared (OPIR) missile-warning system.
“We’re seeing steady exercise with enterprise rising within the army market. Previewing the DoD budgets, we see these and what’s requested and it’s regular wanting ahead,” says Bob Campanini, Vice President of Optoelectronics, for Micropac (Dallas, Texas).
The DoD funding commitments and market pressures are affecting the expansion in rad-hard designs.
“We’re seeing a really numerous and attention-grabbing marketplace for radiation-hardened and radiation-tolerant elements and techniques immediately,” says Ken O’Neill, Affiliate Director, Area and Aviation Advertising and marketing, Microchip Expertise (San Jose, California). “Each section of the market could be very lively in the mean time. There appear to be many various elements at play. U.S. and worldwide funding for human spaceflight, more and more formidable robotic and autonomous missions, elevated precedence on protection early-warning and communications techniques, and business ventures providing earth statement and communications companies are all elements in immediately’s buoyant house market.”
“Designs are always churning. The elevated U.S. funding in army house is driving progress in categorised and unclassified purposes. The small sat enterprise is rising even quicker,” says Anton Quiroz, President of Apogee Semiconductor (Plano, Texas).
Manned missions are additionally getting funding {dollars}. “A number of consideration goes to shorter mission size in sure orbits however there are different longer, manned missions which have pushed loads of testing,” Campanini says. “The architectural method of getting a number of situations of the identical satellite tv for pc drive a pretty quantity manufacturing for constellations. After all, the radiation publicity to units and sign paths does rely on the meant orbit, potential shielding from the bodily construct choices, alternative in radiation tolerant gadget supplies. Supplies resembling fiber optic sign paths seen nice provider advances in radiation tolerance and are inherently resilient to electrical and magnetic fields.”
Lengthy-life categorised missions are nonetheless essential to the U.S. army, however there may be rising demand for shorter-life techniques which might be low-cost and high-performance that may be deployed extra rapidly than a conventional military-satellite mission.
“When electronics is concerned, the ’hottest utility‘ is at all times the very best quantity utility and at the moment that’s the (small sat) LEO constellations,” Campanini says. “A number of of those finish purposes drive the identical/comparable calls for for electronics. LEO small sats and manned house flight have comparable radiation wants (minimal radiation necessities if people are additionally current). Manned missions drive different necessities associated to redundancy, fault tolerance, and fail secure.”
“Navy techniques are exploring the trade-space encompassing mission success, procurement value, and time to launch,” O’Neill says. “Conventional techniques had excessive mission success, however had been costly and took a very long time to construct, check, and launch. Whereas conventional techniques are nonetheless beneath improvement, there are additionally army techniques in improvement which search novel methods to scale back value and improvement time with out sacrificing mission success.” (Determine 1.)

[Figure 1 | Microchip’s portfolio of radiation-hardened and radiation-tolerant solutions includes high performance FPGAs [field-programmable gate arrays], mixed-signal ICs, remoted DC-DC converter modules, customized energy provides, hybrid options, MOSFETS, and extra.]
Provide-chain shortages
The one impediment seemingly slowing this fast progress is the supply-chain scarcity plaguing your entire globe. Orders for elements are coming in, however supply delays abound for every type of components.
“The provision-chain scarcity continues to be haunting the business,” Quiroz notes. “We nonetheless see quotes with 52-week lead instances for sure elements. As a result of this disaster, we see army customs demanding techniques be made within the U.S., with DoD investing extra in long-term onshore semiconductor manufacturing. Constructing this infrastructure in the united stateswill take time, however it can assist and it’s higher late than by no means. The tensions between China and Taiwan are nonetheless a difficulty and a danger issue with an unknown lead to the long run, so this funding is critical. From our perspective, we handle our stock, sustaining IC elements in inventory for key contracts.”
It’s not simply semiconductors which might be on again order, however electronics elements of each kind.
“The delays have expanded to all supplies, ICs, passive elements, mechanical connectors, and extra,” Campanini says. “It should take a complete method to beat these challenges to the army provide chain. Micropac is a part of the Protection Microelectronics Cross Operate Workforce, amongst different consortia, working to beat challenges to the warfighter. The microelectronics offshore problem was not created in a yr and it’ll take greater than a yr to resolve. So sure, there shall be a danger publicity for a couple of extra years.
“Authorities funding will assist, however that may take time to unravel and to flush out any bottlenecks,” Campanini continues. “They’ll wish to ensure it’s not only a knee-jerk response, and that they preserve onshore functionality. It should require offering electronics at decrease value – which is why all the things moved to Taiwan within the first place. Working semiconductor fabs within the U.S. shall be dearer than in Taiwan because of labor and different prices.”
Many suppliers are increasing their services and likewise their workforces to fight the delays, however nobody has but gotten forward of the provision curve:
“We see that our business companions and subcontractors are investing to extend capability and to rent further employees, so we count on that the present provide constraints will ease within the close to future,” O’Neill says. “Despite the fact that longer lead instances on rad-tolerant FPGAs are pushed extra by meeting and screening-cycle instances than by semiconductor wafer availability, we nonetheless welcome authorities funding in home microelectronics manufacturing as it can present us with extra decisions for future generations of merchandise and assist cut back reliance on international sources.”
Some query whether or not authorities funding within the quick time period shall be sufficient.
“The electronics market is fueled by decrease prices and prospects will at all times push for decrease and decrease prices, particularly within the business markets which drives many of the demand for semiconductors.” Campanini says. “Will this lower-cost want push manufacturing offshore once more sooner or later? A extra complete method past merely throwing some cash on the short-term wants could also be wanted to keep away from the long run pendulum swing again to decrease value, offshore manufacturing.
Managing prices and COTS in house
Whereas the provision chain stays a procurement problem, designers are being compelled to innovate to fulfill diminished dimension, weight, energy, and value (SWaP-C) calls for with business off-the-shelf (COTS) whereas sustaining acceptable radiation-tolerance ranges so the techniques don’t fail when hit with cosmic rays.
The demand is for fast deployment of techniques with decrease prices which might be constructed with system-level redundancy reasonably than component-level redundancy, Campanini notes. “This makes it robust to pack in rad-tolerance, however the decrease mission assurance goes together with the constellation structure. On a optimistic aspect, designing these less complicated techniques could be executed extra rapidly than bigger, extra complicated techniques, so you might have a quicker time to deployment.”
There’s a “constant pattern to decrease radiation ranges, however assured at these decrease ranges, in assist of the vastly rising LEO missions,” he continues. “Whereas to not a low sufficient stage to permit use of business or non-radiation hardened elements with out shielding or different system stage mitigation options, there may be an expectation of serious value reductions. Semiconductor suppliers are stepping as much as present decrease radiation efficiency merchandise, usually in plastic packages at considerably decrease prices.
Leveraging business manufacturing may assist conventional rad-hard electronics suppliers mitigate among the challenges with readying COTS elements for house purposes
“To handle the diminished value necessities and demand for COTS elements, we leverage business foundries,” Apogee’s Quiroz says. “For higher-volume purposes like small sats, the worth factors are higher than upscreening. While you upscreen a component, you’re principally wrapping a $100 invoice round it. With a ground-up business silicon course of, you’re bolting on the rad-hard elements utilizing plastic packaging. This lets you reap the benefits of business check flows and tailor the product to an aggressive worth goal and high-volume purposes – those who procure greater than 100,000 models.” (Determine 2.)

[Figure 2 | Apogee Semiconductor’s rad-hard logic family is available at 30 to 300 krads, with plastic and ceramic package flows, for small sat, military space, and commercial missions.]
Microchip has two complementary approaches to the calls for for higher-volume, lower-cost house elements, O’Neill says: “One among our approaches revolves across the idea of ‘Sub-QML’ [qualified manufacturers list] units. This idea takes merchandise which have been designed to offer a excessive stage of radiation tolerance and reduces or eliminates pricey QML testing and screening. The result’s a product line that has the radiation traits and the flight heritage of a conventional QML product line, however with optimized testing and diminished paperwork and a cheaper price level. The second method is the ‘COTS to RT’ idea, which takes business or automotive merchandise and gives further screening and radiation testing to offer assurance on the suitability of the product for deployment in house.”
With the army, nevertheless, it’s by no means a one-size-fits-all method. It at all times comes right down to necessities and it’s a undeniable fact that these necessities – element, system, or platform – are all decided by the mission.
“Rad-hard product prices are pushed by materials prices as rad-hard elements are sometimes 500 to over 1,000 instances dearer than COTS elements. The important thing to leveraging COTS elements for house is to know the true element necessities, why the engineers and procurement officers are shopping for this half,” Campanini explains. “They assist us tailor the certification flows to a COTS stage. Determining what you want and don’t want, understanding the true necessities, permits designs with next-level mitigation schemes to permit using elements with no discount in reliability.” (Determine 3.)
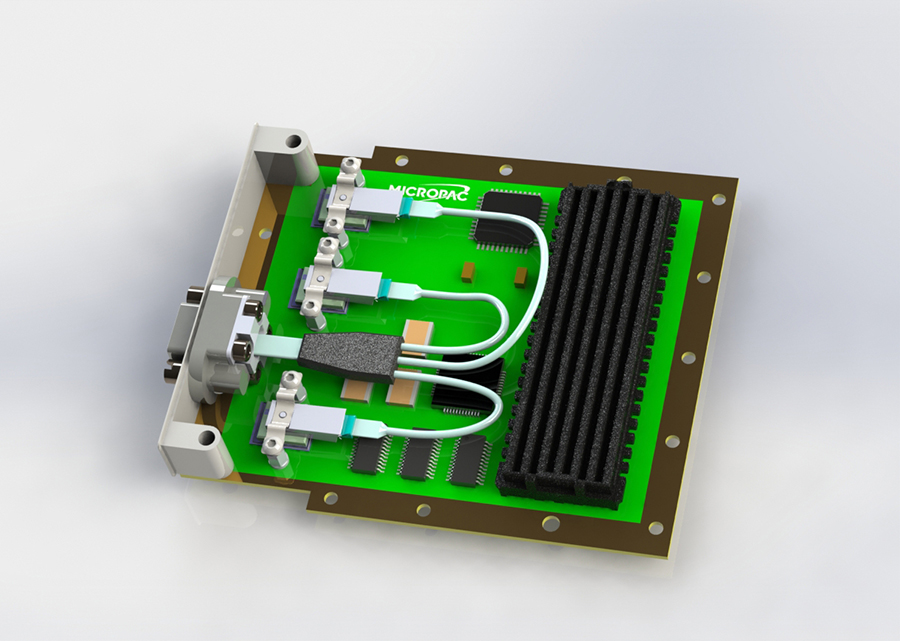
[Figure 3 | Pictured is the Micropac FMC card – high-rel board design.]
Open requirements
Open requirements and architectures are additionally a method for lowering prices and leveraging business expertise for army techniques.
“SpaceVPX and different requirements have been seen throughout many army house prospects,” Campanini says. “Micropac is advancing a Frequent Machine Architecture (CDA) method to standardization.
“The numerous progress in small-sat purposes is immediately fueled by open requirements,” he continues. “The very standardized CubeSat (obtainable as catalog gadgets) to the bigger small sats utilizing commonplace components resembling VPX playing cards and off-the-shelf constructing blocks (batteries, processor playing cards, and so on.) inside customized chassis is gaining in reputation. Quick(er) lead instances and ease of improvement is driving this method.” (For extra on SpaceVPX see the article on web page 12.)
Requirements are additionally being developed and mentioned for packaging of elements. “We’re concerned within the Area Energy Consortium (spacepower.org), which seems to convey business requirements to energy techniques for house exploration,” Quiroz says. “There’s additionally a normal being developed round plastic packaging for house elements. That is occurring inside JEDEC [standards body]. Whereas there’s a commonplace course of round conventional ceramic movement, with army specs that should be met, there may be not one for a plastic movement. As demand for plastic packaged units will increase a normal shall be obligatory to make sure constant efficiency. I believe we’re at the least a yr away from a proper announcement relating to the usual.”
AI innovation in house techniques
Open architectures and business expertise additionally drive innovation in synthetic intelligence (AI) and machine studying (ML), now being utilized in army techniques. Suppliers are seeing elevated necessities for AI options in house techniques.
“There are a couple of firms arising with AI-based options for imaging or different sensor purposes in house techniques,” Quiroz says. “Protection funding is driving a few of this.”
Many preliminary purposes for AI in house are geared towards imaging and different sensor purposes.
“There are lots of explanation why AI is attention-grabbing to builders of house techniques. An instance usually quoted is cloud detection,” O’Neill says. “In an Earth-observation system which seeks to seize photos of objects on the Earth’s floor, photos of the tops of clouds obscuring the bottom or sea beneath are of no use. An AI system that may acknowledge photos as cloud tops and discard them conserves storage capability and downlink bandwidth. There are lots of different examples the place AI can be utilized to preserve sources, or to make autonomous choices on-orbit, eradicating ground-based people from the choice loop, rushing response instances for autonomous or robotic missions, rushing the acquisition of scientific knowledge, or maybe even enabling a fast response throughout a national-security mission.”
Microchip has launched the VectorBlox AI/ML software program improvement package and IP to be used in its FPGAs for image-processing purposes, O’Neill notes. It saves as a lot as 70% energy when in comparison with equal SRAM [static random-access memory] FPGAs. The power to carry out intense AI purposes whereas producing considerably much less warmth than competing options gives a big benefit for house designers, he provides.